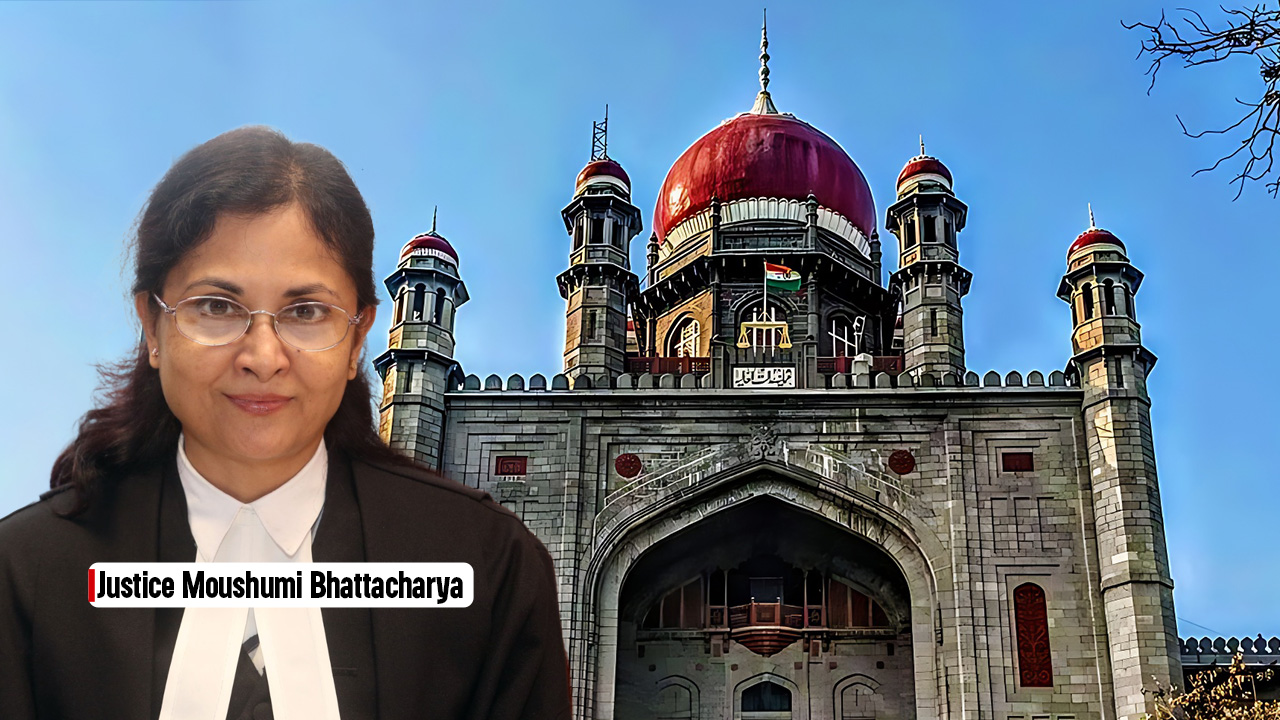
Adjudicating Authority Is Not Bound By The Recommendation Of The Resolution Professional Under Section 99 Of The Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code, 2016 : Karnataka High Court
Live LawA division bench of the Karnataka High Court in its recent judgement/dated April 5, 2022, dismissed a writ petition challenging the constitutional validity of Sections 95, 99 and 100 of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 as it found no merit to the challenge. Background: An application was filed before the Hon'ble National Company Law Tribunal, Bangalore by the Financial Creditor * through the Resolution Professional under Section 95 of the Code for initiation of personal insolvency resolution process against the Personal Guarantor. The said appointment of the Resolution Professional was challenged by the Personal Guarantor by filing a writ petition before the Karnataka High Court, seeking the following: Declaration that Section 95 of the Code is unconstitutional to the extent that it permits the filing of applications through the resolution professional. Arguments The Petitioner contended that under Section 95 of the Code, an application can be filed to initiate insolvency resolution by a creditor through a Resolution Professional. The Court held that the process contemplated under Sections 95 to 100 is a time bound process, which requires the Resolution Professional to firstly give reasons in support of his recommendation.
History of this topic

Annual Digest Of IBC Cases: 2024
Live Law
Application U/S 12A Of IBC Can Be Withdrawn By Resolution Professional Before It Is Heard Or Allowed: NCLAT
Live Law
Non-Admission Of Claim By Resolution Professional Cannot Be Challenged First Time In Appeal Before Appellate Tribunal: NCLAT
Live Law
Adjudicating Authority Cannot Enter Into Merits At S. 95 Application Stage Before Report Of RP Is Submitted U/S 99 Of IBC: NCLAT
Live LawResolution Professional Has Authority To Determine Creditor's Related Party Status: NCLAT
Live Law
NCLAT Rejects Resolution Plan of Bishwanath Traders & Investment Ltd. under Section 29A of IBC
Live Law
Karnataka High Court Disposes Byju Raveendran's Plea After NCLAT Begins Hearing His Appeal Challenging Insolvency Proceedings
Live Law
Insolvency Professional Entities Qualified To Be Appointed As Resolution Professionals: NCLT Mumbai
Live Law
NCLT Kochi: Creditors Can't Initiate Insolvency Proceedings Against Personal Guarantor Without Establishing Independent Default By CD
Live Law
Decision Taken By New Resolution Professional Cannot Be Objected By Erstwhile Resolution Professional: NCLAT Delhi
Live Law
NCLT Chennai - Resolution Professional Should Not Rely Solely On Corporate Debtor's Records For Verifying Claims
Live Law
Section 7 IBC Petition Can't Be Filed By Power Of Attorney Holder Unless Authorized By Board Resolution: NCLT Hyderabad
Live Law
Question Of Value Can't Be Raised Post Approval Of Resolution Plan By CoC: NCLAT Delhi
Live Law
During Pendency Of Liquidation Application, NCLT Kolkata Directs CoC To Re-Vote On Promoter's Rejected Resolution Plan, Since Plan Value Has Been Increased
Live Law
During Pendency Of Liquidation Application, NCLT Kolkata Directs CoC To Re-Vote On Promoter's Rejected Resolution Plan, Since Plan Value Has Been Increased
Live Law
NCLT Has Inherent Power To Recall Order Approving Resolution Plan Which Is Not Submitted As Per IBC : Supreme Court
Live Law
NCLT Kolkata: Revival Of Corporate Debtor Is Primary Goal Of Resolution Plan And Going Concern Sale
Live Law
Resolution Professional Can't Question COC Decision Of Replacement: NCLAT Delhi
Live Law
Supreme Court Upholds Constitutionality Of IBC Provisions Relating To Personal Guarantors; Says Adjudicatory Role Can't Be Read Into Sec 97
Live Law
NCLAT Delhi: Claims Cannot Be Entertained After Approval Of Resolution Plan By CoC Even If Resolution Plan Is Still Pending For Approval By NCLT
Live Law
SC Issues Notice to Centre on Pleas Challenging Provisions of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code
News 18
Resolution Professional Empowered To Keep Claims In Abeyance: NCLAT Chennai
Live Law
New Claims Cannot Be Admitted When Resolution Plan Is Approved By The CoC And Is Pending Before The AA For Approval: NCLT Mumbai Reiterates
Live Law
Approval Of Resolution Does Not Absolve Guarantor; NCLT Mumbai Reiterates
Live Law
Resolution Applicant Wilfully Fails To Implement Plan, NCLT Mumbai Orders Liquidation Without Monitoring Committee’s Mandate
Live Law
No Ipso Facto Absolvement Of Guarantor’s Liability Upon Approval Of Resolution Plan: Allahabad High Court
Live Law
AA Shall Either Approve Or Reject The Resolution Plan, No Power To Modify It: NCLAT Delhi
Live Law
No Fetter, Embargo Or Legal Impediment For A Trust To Be A Resolution Applicant: NCLAT Chennai
Live Law
Erstwhile Resolution Professional Has No Right To Be Heard Before Being Replaced Under Section 27: NCLAT Delhi
Live Law
Issue Of CIRP Cost To Be Decided In COC MEETING, Not By Adjudicating Authority : NCLAT Delhi
Live Law
'Liquidation Last Resort', NCLT Directs COC To Re-Consider The Rejected Resolution Plan: NCLT Mumbai
Live Law
Gujarat High Court Stays IBBI's Order Requiring Resolution Professional To Undergo Pre-Registration Educational Course From IPA
Live Law
Reverse Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process In Case Of Real Estate Companies
Live Law
NCLT Ahmedabad Denies Approval Of Resolution Plan For Being Unimplementable
Live Law
A Report Under Section 99 Of IBC Cannot Be Filed By Resolution Professional Without The Adjudicating Authority's Directions: NCLT Mumbai
Live Law
Resolution Professional Is Only Authorized To Operate Accounts Of Corporate Debtor : NCLAT Chennai
Live Law
NCLT Hyderabad Initiates Insolvency Process Against The Personal Gauartor Of Deccan Chronicle Holdings
Live Law
Claims That Were Not A Part Of The Resolution Plan, Can't Be Claimed After Approval Of The Resolution Plan: NCLT Mumbai Reiterates
Live Law
Corporate Debtor Cannot Be Dragged Into CIRP Mala Fide For Any Purpose Other Than Resolution Of Insolvency: NCLT Mumbai
Live Law
Rejected Claims By Resolution Professional In Insolvency Proceedings, To Be Decided By The Arbitrator: Delhi High Court
Live Law
Project Wise CIRP Of Real Estate Company Is Outside The Purview Of Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code, 2016: NCLT Chennai
Live Law
Weekly Round Up Of IBC Cases: 2nd May To 8th May 2022
Live Law
Resolution Professional Can Submit An Additional Report Under Section 99 Of Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code, 2016: NCLAT
Live Law
MSMEs, Insolvency Resolution Processes & The Avoidance Applications
Live Law
Resolution Professional Cannot Prosecute Preferential Transactions After Approval Of Resolution Plan: NCLT Kolkata
Live Law
Resolution Professional Cannot Decide The Eligibility Under Section 29A Of The Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code, 2016: NCLAT Delhi
Live Law
Commercial Wisdom of the CoC To Prevail, Unless The Same Is In Contravention Of Any Law, Reiterates NCLAT
Live Law
After Approval By The Adjudicating Authority, The Resolution Plan Is No More A Confidential Document: NCLAT
Live Law
The Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code – Respite To MSME
Live LawDiscover Related











![Karnataka High Court Monthly Digest: December 2024 [Citations: 490 - 532]](https://www.livelaw.in/h-upload/2023/03/01/461349-408717-karnataka-high-court-monthly-digest.jpg)












![Calcutta High Court Annual Digest: Part-I [Citations: 1-99]](https://www.livelaw.in/h-upload/2024/12/23/578091-calcutta-high-court-annual-digest-2024.jpg)





![Kerala High Court Monthly Digest: December 2024 [Citations: 766 - 828]](https://www.livelaw.in/h-upload/2024/09/03/559124-750x450519604-750x450456553-408710-kerala-high-court-monthly-digest.jpg)
![Kerala High Court Monthly Digest: December 2024 [Citations: 766 - 828]](https://www.livelaw.in/h-upload/2024/09/03/559124-750x450519604-750x450456553-408710-kerala-high-court-monthly-digest.jpg)