)
COVID Pandemic Has Disrupted Global Value Chains, India Must Reorient Its Trade Policy
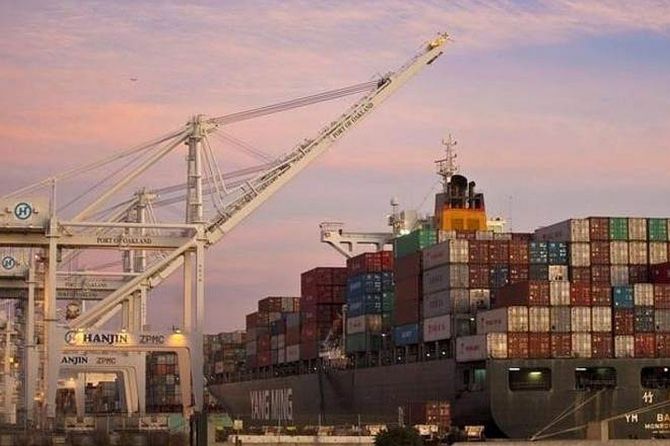
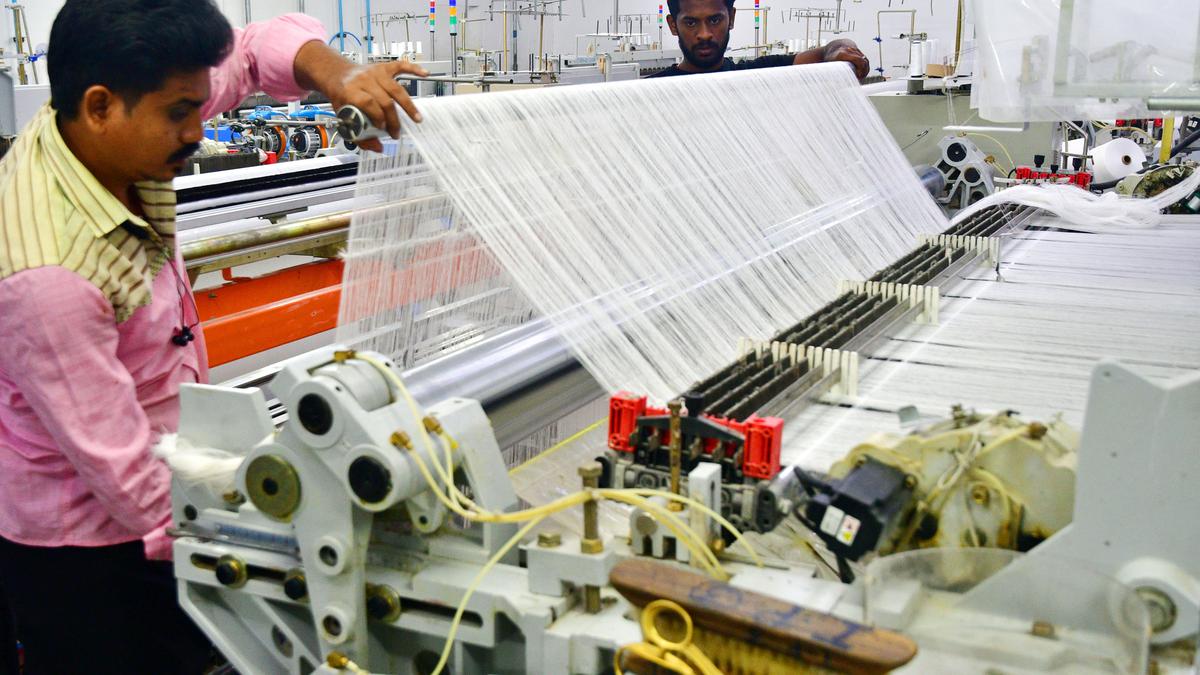
News 18The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed existing vulnerabilities associated with international trade, especially for developing countries that are heavily linked into existing global value chains. Diversification has also occurred in terms of destination markets, with the total share of India’s leading export markets declining from 50 per cent in 2010-11 to 45.5 per cent in 2018-19. However, resource-based exports and low-tech exports continue to dominate India’s export basket; in 2019, 32 per cent of India’s exports were resource-based, followed by 22 per cent of low-tech exports. Similarly, an analysis of several Indian manufacturing firms across sectors over the 2001-2015 period shows that increasing the share of digital assets in a firm’s infrastructure significantly and positively impacted firm-level export intensity. Currently, India lags behind many developing countries in the digitalisation of manufacturing exports; the value added by digital services in India’s exports is largely concentrated in the computer, programming and telecommunication services sectors.
History of this topic

DC Edit | Time to focus on service sector
Deccan Chronicle
India’s exports rise, boosting global presence
Deccan ChronicleDon’t take India’s strong services exports story for granted: Goldman Sachs
The Hindu
Manufacturing versus services: A false binary
Hindustan TimesDC Edit | Inflation, exports still a concern
Deccan Chronicle
Technology will boost the role of MSMEs in India’s export success
Live Mint
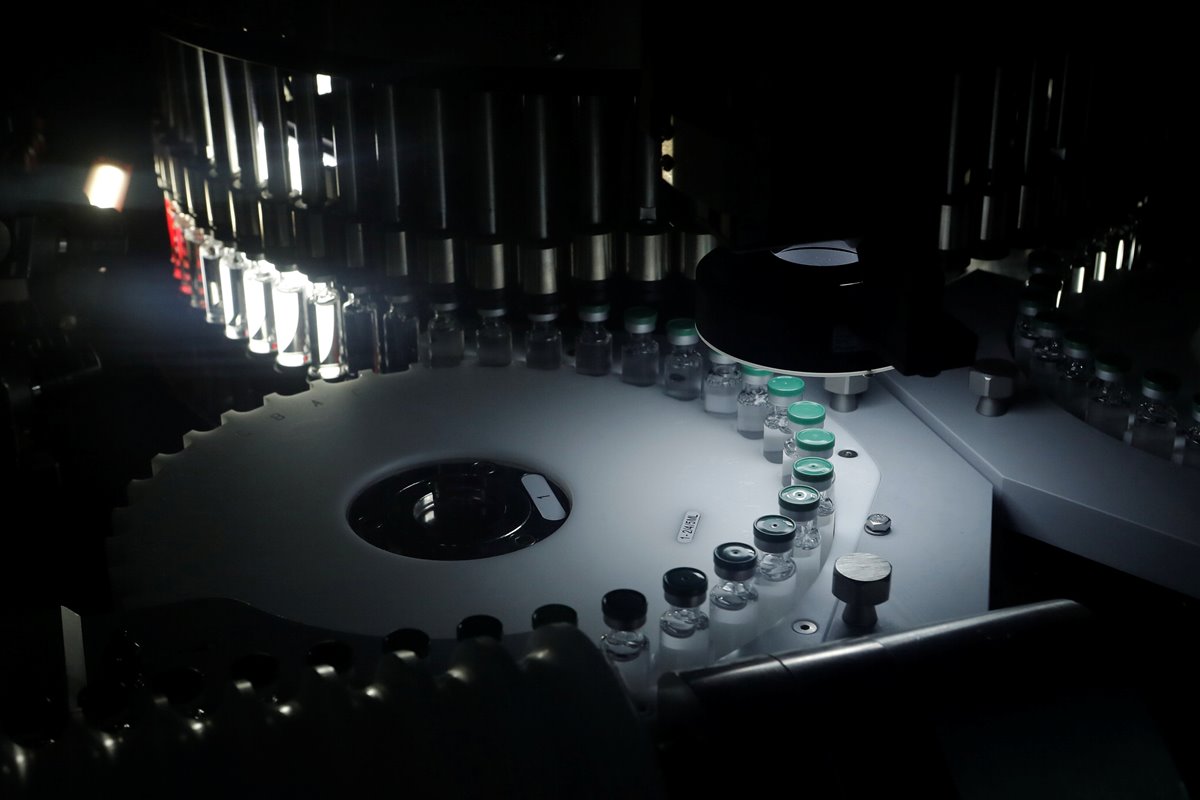
India to resume COVID vaccine exports to COVAX, neighbours
Al Jazeera
Explained: Why India's economy needs a manufacturing push
India Today)
Tap opportunities in post-COVID world to meet $400 billion export target, says PM to heads of Indian missions abroad
Firstpost
India's Covid-19 cases mount but uncertainty over US export ban on vaccine raw materials continues
India TodayIndia’s COVID-19 vaccine export may be curbed
The Hindu)
India Has Shown Great Progress in Reducing Number of Covid-19 Cases, Says WHO Chief
News 18‘Supply chain shift from China may benefit India’
The Hindu
Opinion | Covid and its impact on economy and MSMEs
Live Mint
India’s exports grew 6% in Sep after 6-month decline
Live Mint)
India Exported 23 Lakh PPE to Five Countries Including US, UK & UAE in July: Union Health ministry
News 18
CII calls for early FTP to raise India’s global export share to 5%
Live Mint)
India Remains a Key Contributor to Our Global Supply Chain Despite Economic Turbulence: Boeing
News 18Discover Related












)